Industries
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
In today's rapidly evolving networking landscape, selecting the right single mode transceiver is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in data transmission. According to the latest market report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global optical transceiver market is projected to reach USD 4.47 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 12.8% from 2021.

As organizations increasingly rely on high-speed networks to support applications such as cloud computing and data centers, the demand for single mode transceivers has surged due to their ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal degradation. Properly choosing a single mode transceiver not only enhances network efficiency but also contributes to cost savings by reducing maintenance and operational downtime. Therefore, understanding key criteria such as wavelength, data rate, and compatibility with existing infrastructure is essential for optimizing your networking needs.
Single mode transceivers are pivotal in modern networking, particularly in applications requiring high-bandwidth and long-distance data transmission. They operate using a single light path, allowing signals to travel longer distances without significant loss. According to the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), single mode fibers can support data rates exceeding 100 Gbps over distances of up to 80 kilometers, making them a preferred choice for enterprise networks and telecommunications providers.

When selecting a single mode transceiver, understanding their key features is essential. Important specifications include the transmission distance, the type of connector, and the operating wavelength. For instance, transceivers operating at a wavelength of 1310 nm are typically used for shorter distances, while those at 1550 nm can effectively cover longer spans. A report from Research and Markets indicates that the global fiber optic transceiver market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% from 2021 to 2026, highlighting the increasing demand for robust networking solutions using single mode technology. Additionally, factors like compatibility with existing network infrastructure and power consumption should also be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
When choosing a single mode transceiver for your networking needs, there are several key factors to consider. The first is the transmission distance. Single mode fibers are designed for long-distance communication, typically supporting distances of up to 40 kilometers and beyond. According to a report from the Fiber Optic Association (FOA), single mode fibers can achieve higher bandwidths over longer distances compared to multimode fibers, making them ideal for metropolitan and long-haul applications.
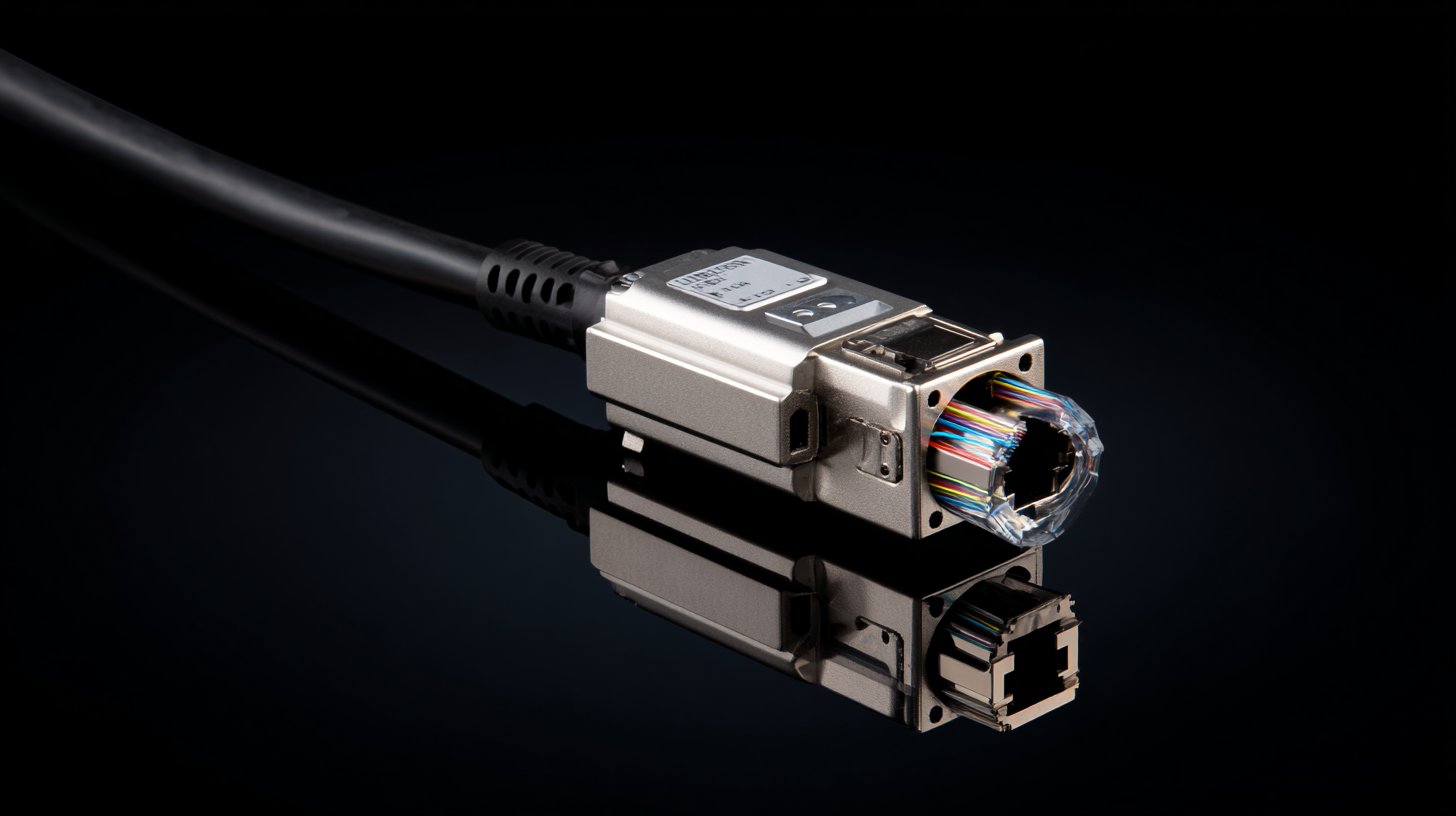

Another critical consideration is the compatibility with existing network infrastructure. Ensuring that your single mode transceiver can interface seamlessly with existing routers, switches, and other optical devices is vital for maintaining network integrity. As per market research by Dell'Oro Group, the demand for single mode transceivers is anticipated to grow significantly due to the increasing need for high-speed internet and cloud services, underscoring the importance of selecting a transceiver that fits well within the broader network ecosystem.
Additionally, the operating temperature and environmental conditions must be factored in. Transceivers typically have a specified temperature range and may require certification for specific environments. According to a study by ResearchAndMarkets, the global optical transceiver market is expected to reach $7 billion by 2025, driven largely by advancements in optical network technologies. Therefore, selecting a transceiver that meets not only your current demands but also future scalability needs is crucial for optimizing performance and reliability.
When selecting the right single mode transceiver for networking needs, it is essential to compare the different types available on the market. Single mode transceivers generally differ based on parameters such as data rates, wavelength, and the specific applications for which they are suited. For instance, SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceivers are popular for their versatility, supporting speeds of up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 10 kilometers, making them ideal for short to moderate-range connections in enterprise networks.
On the other hand, OTN (Optical Transport Network) transceivers are designed for higher capacity applications, supporting data rates of 10 Gbps to even 100 Gbps and are often used in backbone transmission systems. Moreover, considering the wavelength is crucial, as various applications may require different operating wavelengths such as 1310 nm or 1550 nm. Choosing the right transceiver involves assessing the required distance, data rate, and specific network demands to ensure optimal performance and future scalability.
This chart compares different types of single mode transceivers based on their data rates. The data illustrates how the technology has evolved from SFP to QSFP28, with significant increases in data transmission rates.
When selecting a single mode transceiver for your networking needs, assessing compatibility with your existing network infrastructure is crucial. First, consider the type of devices and components already in use, such as routers, switches, and cables. Ensure that the transceiver you choose supports the same standards as your current devices, such as SFP, SFP+, or SFP28, to guarantee optimal performance and interoperability. Mismatched standards can lead to bottlenecks and connectivity issues that undermine network efficiency.
Additionally, evaluate the transmission distance and bandwidth requirements dictated by your current setup. Single mode transceivers are designed for long-distance communication, but the specifications can vary widely. Check the wavelength and the maximum transmission distance supported by both the transceiver and your existing fiber optic cabling. Understanding these parameters will help you select a transceiver that not only fits into your existing infrastructure seamlessly but also enhances network scalability and future-proofing. By ensuring compatibility, you safeguard your investment and maintain the integrity of your network performance.
When selecting a single mode transceiver, evaluating cost efficiency and performance requirements is paramount. The right transceiver can significantly impact your network’s overall speed and reliability. Start by assessing your networking needs: consider the data rates required and the distances that must be covered. Higher data rates often mean higher costs, but if your application demands it, the investment could be justified.
**Tip:** Always compare different manufacturers and models to find the best fit for your budget and performance needs. Check for available certifications and ensure they meet industry standards.
Another factor to consider is the compatibility with your existing network infrastructure. Even if a transceiver offers superior performance, using incompatible equipment could lead to increased costs and network downtime. It’s essential to understand the technical specifications and ensure seamless integration with your switches and routers.
**Tip:** Before making a purchase, try to test the transceiver in your environment, if possible. This hands-on approach can provide insight into performance and help you avoid costly mistakes.
| Transceiver Model | Data Rate (Gbps) | Distance (km) | Wavelength (nm) | Price (USD) | Power Consumption (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 10 | 80 | 1310 | 150 | 2.0 |
| Model B | 25 | 40 | 1550 | 250 | 3.5 |
| Model C | 40 | 10 | 850 | 300 | 4.0 |
| Model D | 100 | 10 | 1310 | 500 | 5.0 |